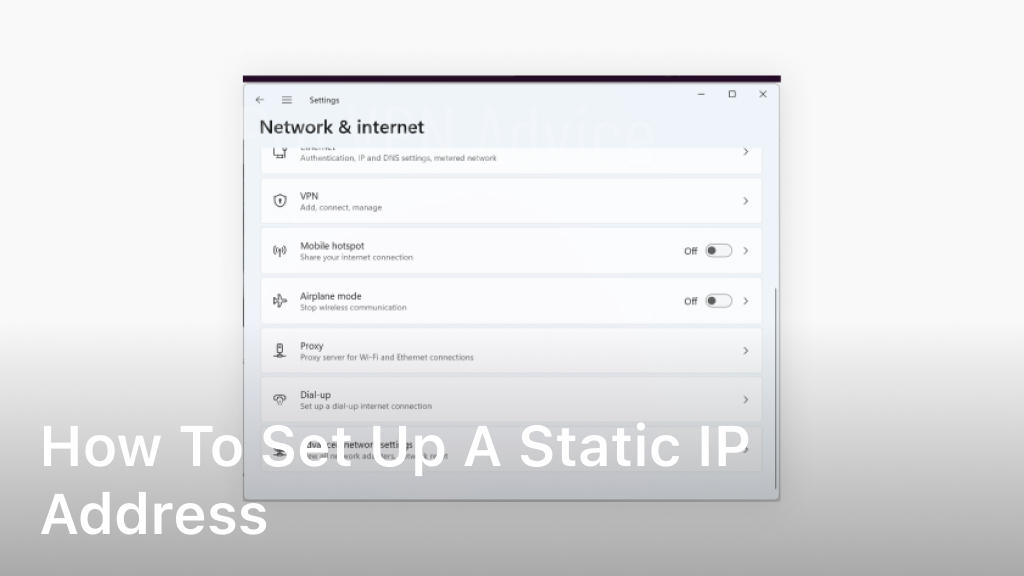
Welcome to our guide on how to set up a static IP address for a consistent network configuration. In this section, we will take you through the step-by-step process, ensuring a secure connection for your network. Whether you’re a Windows or Mac user, we’ve got you covered with specific instructions for each operating system version. So let’s get started and make sure you have a reliable and secure network with a static IP address setup. Understanding Static IP Addresses Before you begin the setup process, it is important to understand what a static IP address is and how it differs from a dynamic IP address. Gain a clear understanding of static IP addresses and their benefits. A static IP address is a fixed address assigned to a device on a network. Unlike dynamic IP addresses, which are automatically assigned by DHCP servers and can change over time, a static IP address remains constant. This means that whenever you connect to the network, your device will always have the same IP address. The main benefit of using a static IP address is that it allows for easier access to network resources and services. With a static IP address, you can easily configure port forwarding, remote access, and networked devices that require a fixed IP address to function properly. It also simplifies the process of setting up virtual private networks (VPNs) and hosting servers. Another advantage of a static IP address is improved security. Since the IP address remains the same, it is easier to set up firewall rules and access controls to allow or deny specific IP addresses. This helps protect your network from unauthorized access and potential security breaches. Furthermore, a static IP address can enhance network performance by reducing connection issues and improving network speeds. Since the IP address is constant, there is no need for the device to request a new IP address each time it connects to the network. This can lead to more reliable and efficient network communication. Overall, understanding static IP addresses is essential before proceeding with the setup process. It allows you to make an informed decision about whether a static IP address is the right choice for your network configuration needs. Checking Network Compatibility Before setting up a static IP address, it is crucial to ensure that your network equipment and devices are compatible with this type of addressing. By checking network compatibility, you can determine if your network supports the assignment of static IP addresses. To check compatibility and make any necessary adjustments, follow the steps below: Access your router’s configuration settings by entering the router’s IP address into your web browser. Typically, the router’s IP address is 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1. However, you can find the specific IP address in the router’s manual or by searching online for your router model. Once you have accessed the router’s configuration settings, navigate to the network settings or LAN settings section. Look for the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) settings. DHCP is responsible for automatically assigning IP addresses to devices on your network. If DHCP is enabled and assigning dynamic IP addresses, you may need to disable it to assign a static IP address. If DHCP is enabled, locate the option to configure a static IP address. This option may be labelled as “Static IP,” “Fixed IP,” or “Manual IP.” Enable this option to assign a static IP address to your device. Save the changes and exit the router’s configuration settings. Your network is now ready to assign static IP addresses. By verifying network compatibility and making the necessary adjustments, you can proceed with confidence to the next steps of setting up a fixed IP address. Obtaining Network Information Setting up a static IP address requires gathering specific network information. By following the steps outlined in this section, you will obtain crucial details such as the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server information. This information is essential for configuring your static IP address correctly. Gathering IP Address Information: The first piece of information you need is the IP address for your device. To find this information: On Windows: Open the Command Prompt and type ‘ipconfig’ to display your IP address. On Mac: Go to the Apple menu, select System Preferences, click on Network, and find your IP address under the Status section. Determining Subnet Mask and Gateway: The subnet mask and gateway are necessary for routing network traffic. Follow these steps to locate these details: On Windows: In the Command Prompt, type ‘ipconfig/all’ to identify the subnet mask and gateway. On Mac: In the Network section of System Preferences, click on Advanced and select the TCP/IP tab to find the subnet mask and router information. Identifying DNS Server Information: The DNS (Domain Name System) server converts domain names into IP addresses. Obtain the DNS server information using the following steps: On Windows: In the Command Prompt, type ‘ipconfig/all’ and locate the DNS server details. On Mac: In the Network section of System Preferences, click on Advanced, select the DNS tab, and note the DNS server IP addresses listed. With this network information in hand, you are now ready to proceed with configuring your static IP address. The next section will provide detailed instructions tailored to your operating system, whether you are using Windows or macOS. Configuring Static IP on Windows Setting up a fixed IP address on your Windows operating system is a straightforward process. Whether you’re using Windows 10, 8, or 7, follow our step-by-step instructions below to configure a static IP. Step 1: Access Network and Internet Settings Open the Start menu and click on the Settings icon. From the Settings window, select “Network & Internet.” Step 2: Go to Network Settings In the Network & Internet window, click on “Network and Sharing Center” to access the network settings. Step 3: Open Network Connections In the Network and Sharing Center, click on “Change adapter settings” in the left-hand sidebar. This will open the Network Connections window. Step 4: Select Network